Welcome to (International Stories). In this story, we will discuss Schizophrenia meaning- 7 Symptoms of schizophrenia. I hope you will like this article.
Schizophrenia meaning-7 Symptoms of schizophrenia
Schizophrenia meaning is a mental illness in which 7 Symptoms of schizophrenia the patient’s personality becomes fragmented as a result of which the ability to think, understand, feel and express emotions is affected.
Schizophrenia is a chronic mental disorder characterized by a combination of symptoms, including hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking and speech, social withdrawal, and impaired cognitive abilities. It affects approximately 1% of the global population and typically emerges in late adolescence or early adulthood.
The causes of schizophrenia are complex and not fully understood. While there is a significant genetic component, it is important to note that genetics alone do not determine the development of the disorder. Multiple factors, including environmental influences, brain chemistry, and psychological factors, also play a role.
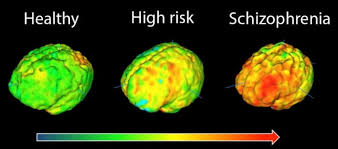
Genetic research suggests that schizophrenia has a strong genetic basis, with estimates indicating that genetic factors account for about 80% of the risk for developing the disorder. However, it is important to understand that having a genetic predisposition does not guarantee that an individual will develop schizophrenia. Rather, it increases the vulnerability to the disorder.
Several genes have been implicated in schizophrenia, and research in this area is ongoing. The DISC1 gene (disrupted in schizophrenia 1) was one of the first genes identified as a potential risk factor. Other genes, such as COMT (catechol-O-methyltransferase) and Neuregulin 1 (NRG1), have also been associated with schizophrenia. These genes are involved in various brain functions, including neurotransmitter regulation, synaptic plasticity, and neurodevelopment.
It is important to note that the genetic causes of schizophrenia are likely to be complex, involving multiple genes and gene-environment interactions. Researchers continue to investigate and unravel the specific genetic mechanisms involved in the development of schizophrenia to deepen our understanding of the disorder and potentially develop more targeted treatments.
Professor Dr. Raza Rahman
A mental condition called schizophrenia causes problems with thinking, understanding, feeling, and expressing emotions. As a result, the patient’s personality becomes disjointed. Recent studies have revealed that schizophrenia is often an intellectual illness.
Affects people. It is a complex disease, but in our society there are unrealistic concepts related to this disease, so the basic information about schizophrenia is being listed below, so that the patient should be treated by a qualified psychologist rather than believing they are under the control of a ghost or other supernatural being.
7 Symptoms of schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a common illness, affecting one percent of the population in any country.
There are about one percent of patients with schizophrenia in Pakistan. There are many symptoms of this disease. For instance, hearing invisible voices, harbouring doubts and suspicions, being disorganised in one’s thoughts and speech, talking to oneself, being obstinate, being lost, keeping a distance from others, having the proper attitude or behaviour.
Schizophrenia is a complex mental disorder that affects a person’s perception, thoughts, emotions, and behavior. While the symptoms can vary from person to person, here are seven common symptoms associated with schizophrenia:
- Delusions: Delusions are erroneous ideas that are unfounded in reality.
People with schizophrenia may experience delusions of persecution, grandiosity, or paranoia, believing that others are out to harm them or that they have special powers or abilities. - Hallucinations: These involve perceiving things that are not actually present in reality. Auditory hallucinations, such as hearing voices, are the most common type experienced by individuals with schizophrenia. However, hallucinations can also entail sensing or experiencing nonexistent tastes, smells, or sensations.
- Disorganized thinking: Schizophrenia can disrupt a person’s thought processes, leading to disorganized thinking patterns. This can result in difficulties in organizing thoughts, making coherent sentences, or connecting ideas logically. Speech may become incoherent or tangential.
- Abnormal motor behavior: Schizophrenia may manifest in abnormal motor behavior. This can include repetitive, purposeless movements, catatonia (immobility or extreme rigidity), or unusual postures.
- Negative symptoms: Negative symptoms refer to a decrease or absence of normal behaviors or emotions. This can include reduced motivation, social withdrawal, lack of emotional expression, diminished speech, and an overall decrease in daily functioning.
- Cognitive difficulties: Schizophrenia can impact cognitive functioning, resulting in problems with memory, attention, problem-solving, and decision-making. It may become challenging for individuals to concentrate or engage in complex tasks.
- Emotional disturbances: People with schizophrenia may experience disruptions in their emotional experiences and expressions. They may have difficulty expressing or recognizing emotions appropriately, resulting in inappropriate or blunted emotional responses.
It’s important to note that schizophrenia symptoms can vary in severity and may come and go over time. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms associated with schizophrenia, it’s crucial to seek professional help from a mental health provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Additionally, many patients struggle to articulate their feelings, lack excitement and desire, and are unable to care for themselves.
Which occurs in the first two years of the disease. Early treatment of this disease is the key to successful treatment.
Reasons:
The origins of schizophrenia are the subject of several hypotheses. While additional reasons for this disease include its impact on the family, early exposure, and environmental variables, it is believed that genetic, developmental, and environmental factors play a vital part in its development difficulties or mental stress. Confrontation and drug use etc. are included.
Treatment:
It is a chronic condition that is curable. The success of treatment depends on starting early, because over time the mental capacity of patients with schizophrenia is severely affected, which is irreversible. This impairment occurs in the early years of the disease.
Therefore, don’t wait to consult a psychiatrist if you or a loved one is showing signs of schizophrenia; otherwise, we risk becoming incurable.
There was no effective therapy for this illness a few decades ago, but today there are numerous effective medications accessible, and their usage reduces the likelihood of complications and improves patients’ quality of life. Keep in mind that family and social support are equally as crucial as drug-assisted psychotherapy.
Embarrassment of illness:
Patients are discriminated against since mental illness is seen as a source of shame not just in Pakistan but also in other nations.
Remember, schizophrenia is not a personal weakness or a character disorder, but a medical disease, the treatment of which is indispensable.
Special attention should be paid. Although there are numerous facilities accessible in our nation for people with schizophrenia and their families, there aren’t many that are actually needed.
Furthermore, the majority of individuals with schizophrenia do not have access to current, evidence-based therapies because of a lack of knowledge, which leads to these people being directed to so-called quacks, and quacks for treatment.
Most of these individuals, it has been discovered, live in extremely unfavourable circumstances.
Numerous homeless persons may be seen walking the streets. These patients are frequently sent to dargahs for treatment, but this just causes the patient’s condition to worsen.
Instead of risking the patient’s life, quick treatment is required.
Consult an experienced psychiatrist, so that with timely treatment, patients can lead a better life.
Schizophrenia is a complex mental disorder that is likely caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. While the exact causes of schizophrenia are still not fully understood, research suggests that genetics play a significant role in its development.
Here are some key points regarding the genetic causes of schizophrenia:
- Heritability: Schizophrenia has a significant genetic component, as evidenced by family and twin studies. People who have a first-degree relative (parent or sibling) with schizophrenia have a higher risk of developing the disorder compared to the general population. The risk increases further if both parents have schizophrenia.
- Polygenic Nature: Schizophrenia is considered a polygenic disorder, meaning that multiple genes are involved in its development. Researchers have identified several genetic variations, or variants, that are associated with an increased risk of developing schizophrenia. These variants are involved in various biological processes, including neurotransmitter function, brain development, and immune system regulation.
- Rare Genetic Mutations: In addition to common genetic variants, rare genetic mutations can also contribute to schizophrenia. Certain rare genetic mutations, such as copy number variations (CNVs) and chromosomal abnormalities, have been associated with an increased risk of developing the disorder. However, these mutations are relatively uncommon and account for a small proportion of schizophrenia cases.
- Gene-Environment Interactions: It’s important to note that genetics alone do not determine whether a person will develop schizophrenia. Environmental factors, such as prenatal complications, exposure to certain infections, stress, and substance abuse, can interact with genetic predisposition to increase the risk. The interplay between genetic and environmental factors is complex and not fully understood.
- Complex Genetic Architecture: Identifying specific genes that contribute to schizophrenia has been challenging due to its complex genetic architecture. The disorder likely involves the combined effects of multiple genes, each with a small individual impact. Moreover, genetic factors may interact with each other and with environmental factors to influence the risk.
It’s important to remember that having a genetic predisposition to schizophrenia does not guarantee that an individual will develop the disorder. Many people with a family history of schizophrenia never experience symptoms, while others without a family history can develop the condition. The interplay between genetic and environmental factors in the development of schizophrenia is an area of ongoing research.
Types of schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a complex mental disorder that is characterized by a range of symptoms, including hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking and speech, social withdrawal, and cognitive impairments. While there is no universally agreed-upon classification system for types of schizophrenia, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), which is widely used by mental health professionals, recognizes different subtypes based on the predominant symptoms present. Here are the subtypes of schizophrenia as outlined in the DSM-5:
- Paranoid Type: This subtype is characterized by prominent delusions and auditory hallucinations. Individuals with paranoid schizophrenia often have persecutory or grandiose delusions and may experience hallucinations that are related to the delusions.
- Disorganized Type: This subtype involves disorganized speech, behavior, and affect. People with disorganized schizophrenia may exhibit incoherent or illogical speech, inappropriate emotional responses, and disorganized behaviors. They may also experience hallucinations and delusions, but they are not as prominent as in the paranoid type.
- Catatonic Type: Disturbances in mobility are what this subtype is distinguished by. People with catatonic schizophrenia may exhibit unusual motor behaviors, such as maintaining rigid or bizarre postures, resisting instructions, and showing repetitive or purposeless movements. They may also experience extreme negativism or mutism.
- Undifferentiated Type: This subtype is used when the symptoms do not clearly fit into any of the above categories or when there is a mixture of symptoms from different subtypes.
- Residual Type: This subtype is used when the individual has experienced at least one episode of schizophrenia but currently does not have prominent positive symptoms (such as hallucinations or delusions). However, they may exhibit milder forms of negative symptoms, such as social withdrawal or impaired thinking.
It is important to note that the DSM-5 no longer includes the subtypes of schizophrenia as criteria for diagnosis. Instead, it emphasizes the individual’s symptom profile and severity. This reflects a shift in understanding schizophrenia as a spectrum disorder with varying symptom presentations and severity levels. Mental health professionals may still refer to the subtypes for descriptive purposes or clinical discussions, but they are not used as formal diagnostic categories.
CONCLUSION:
Preventing schizophrenia is a complex challenge because the exact causes of the disorder are not fully understood. However, there are several strategies that can help reduce the risk or mitigate the impact of schizophrenia. It’s important to note that these strategies may not guarantee prevention, but they can contribute to overall mental well-being and potentially lower the risk of developing the disorder. Here are some approaches:
- Early intervention: Detecting and treating schizophrenia at its earliest stages can improve outcomes. Education and awareness programs should focus on recognizing early signs and symptoms, and individuals showing potential signs should be encouraged to seek professional help.
- Access to mental health care: Ensuring widespread availability of affordable and accessible mental health services is crucial. This includes regular check-ups, counseling, therapy, and medication when necessary. Adequate mental health support can help manage symptoms and prevent exacerbation.
- Reducing stress: High levels of stress have been linked to an increased risk of schizophrenia. Encouraging healthy coping mechanisms, such as exercise, mindfulness, relaxation techniques, and social support, can help individuals manage stress and potentially reduce the risk.
- Substance abuse prevention: Substance abuse, particularly cannabis and hallucinogenic drugs, has been associated with an increased risk of developing schizophrenia. Promoting drug and alcohol education, implementing policies to restrict access to harmful substances, and providing addiction treatment services can help reduce the risk.
- Healthy lifestyle choices: Promoting a healthy lifestyle can have a positive impact on mental health. Encouraging regular exercise, a balanced diet, sufficient sleep, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to overall well-being and potentially reduce the risk of developing schizophrenia.
- Social support and community integration: Creating supportive environments and strong social networks can be protective against mental health disorders. Community-based initiatives that foster inclusivity, reduce stigma, and provide support networks can contribute to overall mental well-being.
- Early childhood interventions: Early interventions targeting childhood development and mental health can potentially have a long-term impact on preventing mental disorders. Implementing programs that promote positive parenting, early detection of developmental delays, and access to quality education and healthcare can be beneficial.
It’s important to remember that while these strategies can potentially reduce the risk of developing schizophrenia, the disorder is complex and multifactorial. More research is needed to better understand the causes and risk factors associated with schizophrenia, which will help inform more effective preventive measures in the future.
FAQ:
Definition of schizophrenia?
A person’s thinking, emotions, and behaviour are all impacted by schizophrenia, a severe and long-lasting mental condition.
It is characterized by a combination of symptoms that can include hallucinations (perceiving things that are not real), delusions (strongly held beliefs that are not based in reality), disorganized thinking and speech, social withdrawal, reduced emotional expression, and cognitive difficulties.
Schizophrenia patients frequently suffer a loss of touch with reality and may struggle to tell what is genuine from what is not.
The disorder typically emerges in late adolescence or early adulthood and can have a profound impact on a person’s daily functioning, relationships, and overall quality of life.
Although the precise origin of schizophrenia is unknown, a confluence of genetic, environmental, and neurochemical variables is thought to be responsible. Treatment for schizophrenia usually involves a combination of antipsychotic medications, psychotherapy, and support services aimed at managing symptoms, improving functioning, and enhancing overall well-being. Many people with schizophrenia may have fulfilling lives with the right care and assistance.
What are the top 5 signs of schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a complex mental disorder characterized by a combination of symptoms that can vary among individuals. It’s important to note that only a qualified healthcare professional can diagnose schizophrenia based on a thorough evaluation. However, here are five common signs or symptoms that are often associated with schizophrenia:
- Delusions: Delusions are false beliefs that are not based on reality. People with schizophrenia may experience paranoid delusions, such as believing that others are plotting against them or that they are being spied on.
- Hallucinations: Hallucinations involve perceiving things that are not actually present. Auditory hallucinations, where individuals hear voices that others cannot hear, are a common symptom of schizophrenia. Visual hallucinations are also possible but less common.
- Disorganized thinking and speech: People with schizophrenia may have difficulty organizing their thoughts and expressing them coherently. Their speech may become disorganized, with abrupt changes in topic or difficulty staying on track during conversations.
- Negative symptoms: Negative symptoms refer to a decrease or absence of normal behaviors or emotions. These may include reduced emotional expression, social withdrawal, diminished motivation, and a lack of interest or pleasure in activities that were once enjoyable.
- Cognitive impairments: Schizophrenia can affect cognitive functions such as attention, memory, and problem-solving abilities. Individuals may experience difficulties with concentration, memory recall, and executive functioning.
It’s worth noting that these signs can vary in intensity and may come and go over time. If you or someone you know is experiencing any concerning symptoms, it’s important to seek professional help from a mental health specialist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Can a schizophrenic live a normal life with medication?
Yes, with the right treatment and support, many individuals with schizophrenia can lead normal and fulfilling lives. Medication is a fundamental component of schizophrenia treatment, and it can help manage symptoms and reduce the frequency and severity of psychotic episodes. Antipsychotic medications are commonly prescribed to control hallucinations, delusions, and other symptoms associated with schizophrenia.
However, it’s important to note that medication alone may not be sufficient. Comprehensive treatment plans typically involve a combination of medication, therapy, and psychosocial support. Therapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) or family therapy, can help individuals develop coping strategies, improve social skills, and enhance their overall functioning. Psychosocial support, including vocational training, housing assistance, and community services, can also contribute to a person’s ability to live a fulfilling life.
It’s worth mentioning that the effectiveness of treatment can vary from person to person, and some individuals may require adjustments to their medication or additional interventions to achieve stability. Regular communication with healthcare professionals and adherence to the prescribed treatment plan are crucial for managing the condition effectively.
While schizophrenia can present challenges, many individuals with the disorder can lead meaningful lives, pursue education and employment, maintain relationships, and engage in activities they enjoy. Each person’s experience with schizophrenia is unique, and it’s important to approach treatment on an individual basis to optimize outcomes and support their well-being.
What are 3 coping strategies for schizophrenia?
Coping strategies for schizophrenia can vary from person to person, as everyone’s experience with the condition is unique. However, here are three common coping strategies that individuals with schizophrenia may find helpful:
- Medication adherence: Consistently taking prescribed antipsychotic medications as directed by a healthcare professional is crucial in managing symptoms of schizophrenia. These drugs can lessen delusions, hallucinations, and other psychotic symptoms. Adhering to the prescribed medication regimen can promote stability and improve overall well-being.
- Psychoeducation and support: Educating yourself and seeking support from mental health professionals, family, and support groups can be beneficial. Learning about schizophrenia, understanding the symptoms and treatment options, and staying informed about the latest research can empower individuals and their families to make informed decisions and better manage the condition. Support groups provide an opportunity to connect with others who share similar experiences and can offer practical advice, empathy, and encouragement.
- Developing coping skills and self-care routines: Engaging in activities that promote mental and emotional well-being can help individuals cope with the challenges of schizophrenia. This may include practicing stress management techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, or relaxation techniques. Engaging in regular physical exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, and managing stress levels can also contribute to overall mental well-being. Additionally, pursuing hobbies, creative outlets, or engaging in activities that bring joy and a sense of accomplishment can be helpful in maintaining a positive mindset.
Remember, it is essential for individuals with schizophrenia to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan and coping strategies that suit their specific needs and circumstances.
A Woman Purchased Parrot at the Bird Shop